|
RGD
- Reduction Gas Detector
|
57
|
|
 |
|
The SRI reduction gas detector is sensitive to volatile reducing compounds down to the ppb level, and is often used to detect atmospheric carbon monoxide and hydrogen. When compared to the FID detector, the RGD is ten times more sensitive to unsaturated hydrocarbons, and virtually unresponsive to saturated hydrocarbons. This combination of sensitivity and selectivity allows the analysis of atmospheric pollutants such as ethylene, benzene, carbonyl sulfide, phosphine, and methanol. |
High concentrations of chlorinated and aromatic compounds can easily contaminate the mercuric oxide bed, resulting in the need for replacement. Reaction tubes are easily replaceable, and blank reaction tubes can be economically packed by the user.
| This four minute chromatogram shows the RGD response to 0.1 mL of 100 ppm hydrogen. | 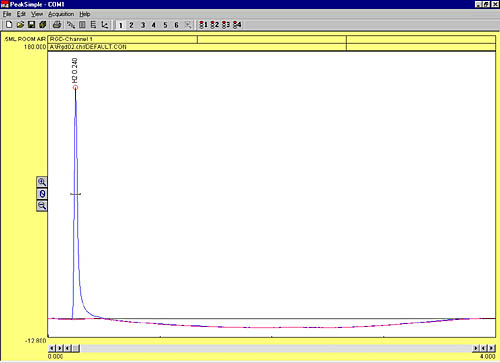 |
| This four minute chromatogram shows the RGD response to 0.5 mL of room air. | 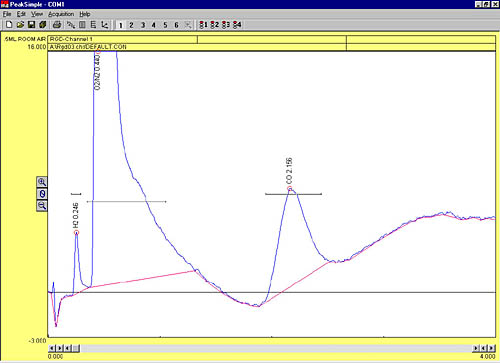 |
|
8690-0009
|
RGD
detector
|
£5,448.00
|
|||
|
8670-0009
|
Blank
reaction tube and sealing frits
|
£96.00
|
|||